In the realm of merchandise management, the term "reorder level" might sound technical, but its essence is straightforward. It's the inventory threshold that triggers a new order for a particular product. In simpler terms, it's the "low fuel" warning light for your stock, signalling that it's time to replenish before you run out completely. However, if the company places an order too late, it would result in stock-out costs, for example lost sales, etc. Continuous review systems monitor inventory constantly and place orders as soon as levels hit the reorder point, requiring sophisticated tracking systems but offering up-to-date control.
What are the factors involved when fixing the reorder level of stock?
- Then we’ll cover how to handle reorder points when you have multiple vendors.
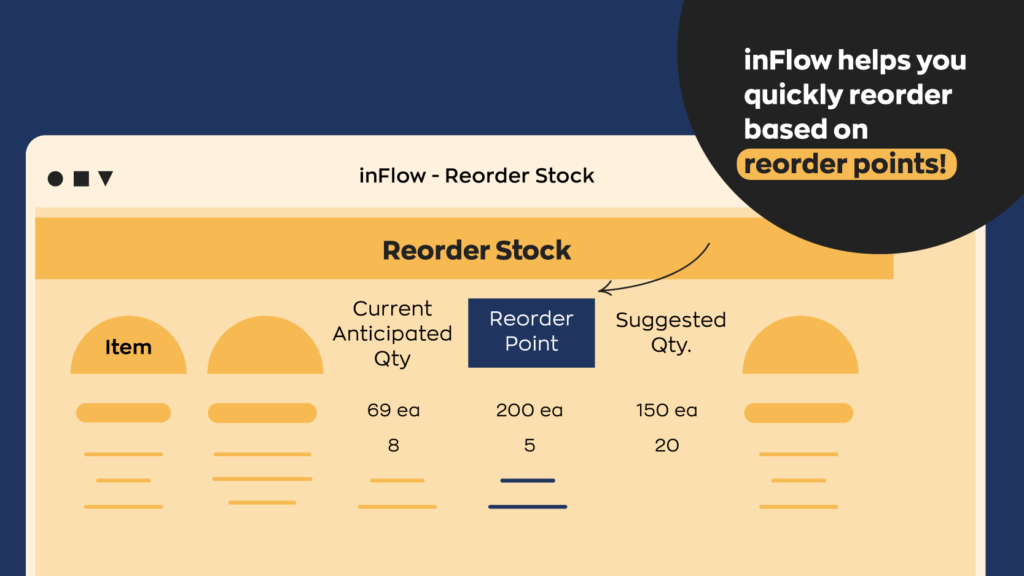
- In most cases, each SKU will have a specific reorder point, which is met when the number of SKUs in storage falls to a predetermined level.
- It saves holding costs and prevents stockouts, overstocking, and lost sales by ensuring that sufficient stock is always available in your inventory.
- Next, Average Daily Usage (ADU), the typical daily consumption or sales of an item, helps gauge inventory depletion rates.
- Some inventory management tools also enable businesses to generate customized reports on inventory stock by item, vendor, delivery date, assembly, and more.
By reordering before you've run out of inventory, you ensure you don't have a gap in the products and services you can offer customers. For example, if there’s a supply chain interruption, you may need to rework your formula, give more lead time, and order more often. If sales are unusually slow or impacted by seasonality, you may need to hold off on reordering. Knowing [your] business, including target, risk, and cost, is the first and necessary step [to setting reorder points].
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
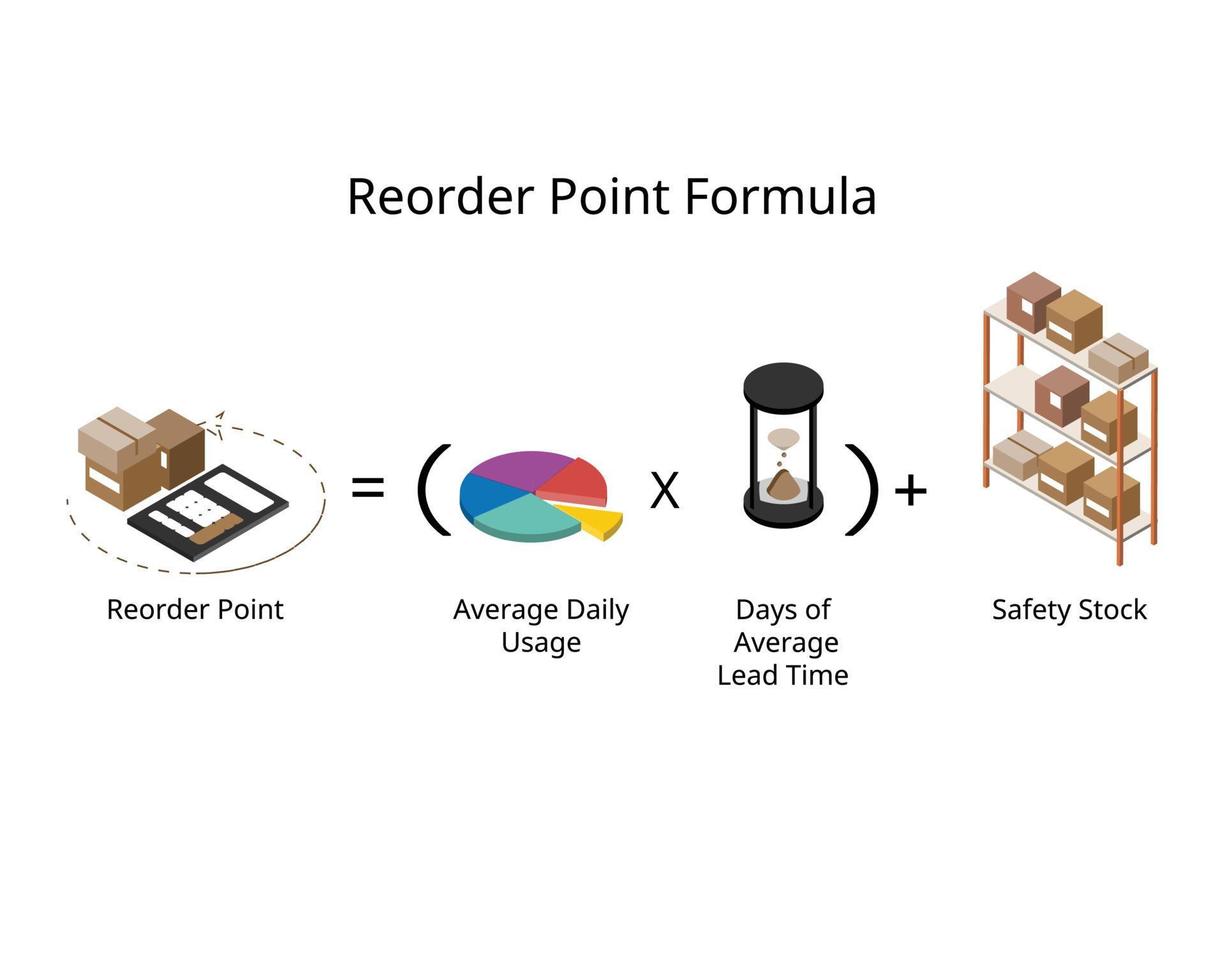
With accurate reorder points for all of your product SKUs, you can meet customer demand in a timely fashion to improve cash flow and avoid the bloated costs of overstock. Shopify POS, for example, calculates ideal reorder points for products based on supplier lead times and the average number of sales per day. This ensures you know which products are running low on stock and have enough lead time to replenish inventory before quantities reach zero. Businesses which follow lean inventory practices or a just-in-time management strategy usually don’t have safety stock. In such cases, your reorder point can be calculated by multiplying your daily average sales by your lead time.
Definition of Re-Order Quantity (ROQ)
Utilizing these structured steps will facilitate accurate reorder level calculations, ensuring efficient inventory management and reducing the risk of disruptions due to inventory shortages or excess. ShipBob is an order fulfillment solution that features built-in inventory management software, giving you precise control over your inventory. You can check inventory counts at each fulfillment center and set automatic reorder levels, so you are notified when stock is running low.
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning promise greater precision and adaptability in what are dilutive securities dilutive securities meaning and definition management. Businesses that stay updated with these developments and adapt their strategies accordingly will be well-positioned to thrive in competitive markets. In conclusion, mastering reorder level management is an ongoing process requiring attention, analysis, and adaptation.
If you don’t update your inventory timely and adequately, you’re inviting the risk of going out of stock during high demand. For example, you could keep 15 extra chairs, 3 days’ worth of products, in stock in case the shipment arrives late. If you wait to order until you have run out of inventory, then there will be a lag between when you place the order and when you can sell your new inventory. Setting a reorder point can help you reorder in time to avoid this availability gap.
Over those three months (or 92 days) that averages out to 1.5 units sold on average per day. The reorder point formula shows what happens in an ideal scenario, but things may work out differently in practice than they do in theory. Now we’ll plug the figures from our example into the reorder point formula.
By applying the principles and strategies outlined in this guide, businesses can optimise inventory management, leading to improved operational efficiency and success. Seasonal fluctuations require adjustments to account for predictable variations, such as increased sunscreen sales in summer. Long-term trends, marketing activities, competition, and changes in the product life cycle also impact demand and necessitate corresponding adjustments. Safety Stock is extra inventory to cushion against demand variability and supply issues, such as unexpected demand spikes, supplier delays, and quality problems.
The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. Therefore, Re-Order Quantity should be fixed in such a manner that the sum of carrying cost and ordering cost is the least. This written account will help you understand the major differences between re-order level and re-order quantity.
Implement temporary adjustment factors, such as multipliers or additives, to reorder levels during seasonal peaks, gradually modifying them as the season progresses. Employ rolling horizon planning, which looks several seasons ahead and regularly updates plans with new information. On the other hand, a dynamic reorder level adjusts based on changing conditions like demand fluctuations, lead time variations, or seasonal factors. This method uses real-time data and forecasting techniques to vary both the reorder point and the order quantity.

